Copyright is the right to copy and publish a particular work. The terms “copy” and “publish” are quite broad.”Publish” and “copy” have quite broad definitions. These include electronic copying, translating, making a television show based on the book, and publishing the material online. Copyright applies to works that are literary or creative in nature.’
Almost all works of creative and unique endeavour are included in this generic term. Only an idea’s precise expression is shielded by copyright; the concept itself is not protected. If the process of gathering the information requires creative effort, the collection of facts can be protected by copyright. Although some nations offer distinct protection for sets of information that meet the criteria for being called “databases,” this provision is not regarded as copyright. The work is automatically protected by copyright at the time of creation. Additional benefits, such as the right to sue or increase your damages award, can be obtained in some countries by registering with a copyright office. Once an artwork’s copyright period expires, it enters the public domain.
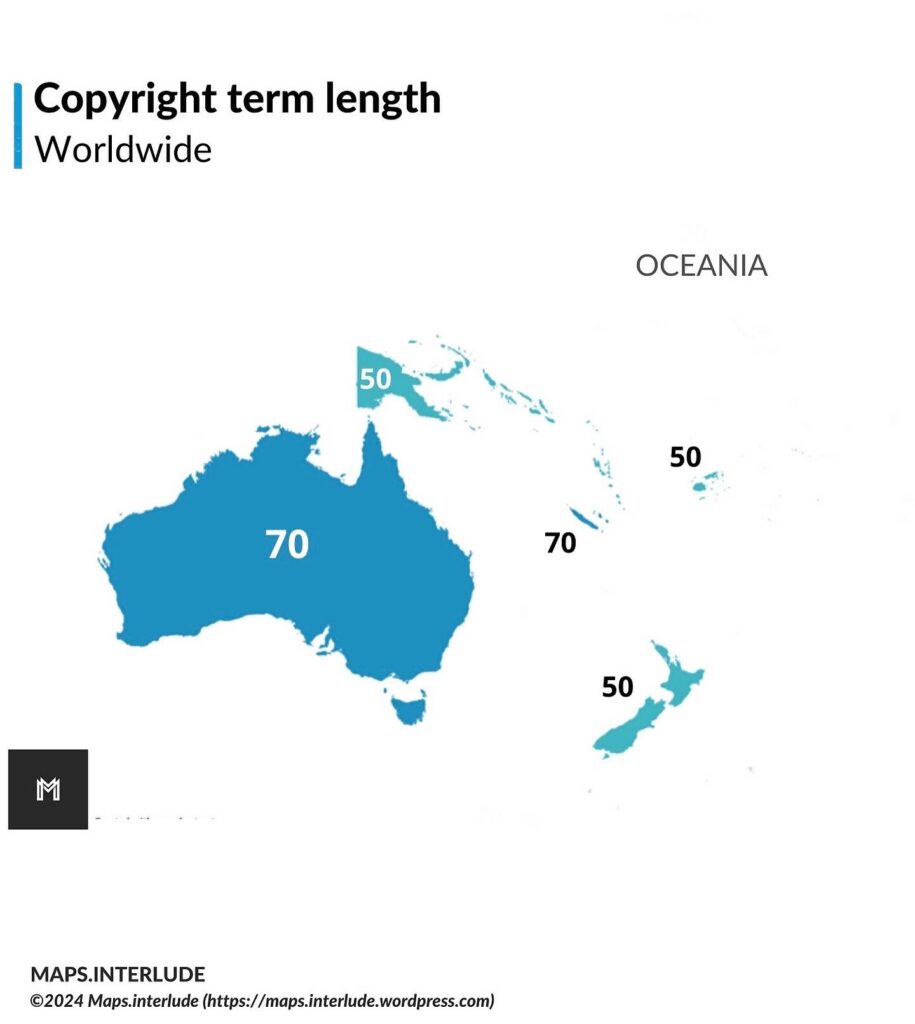
Berne Convention
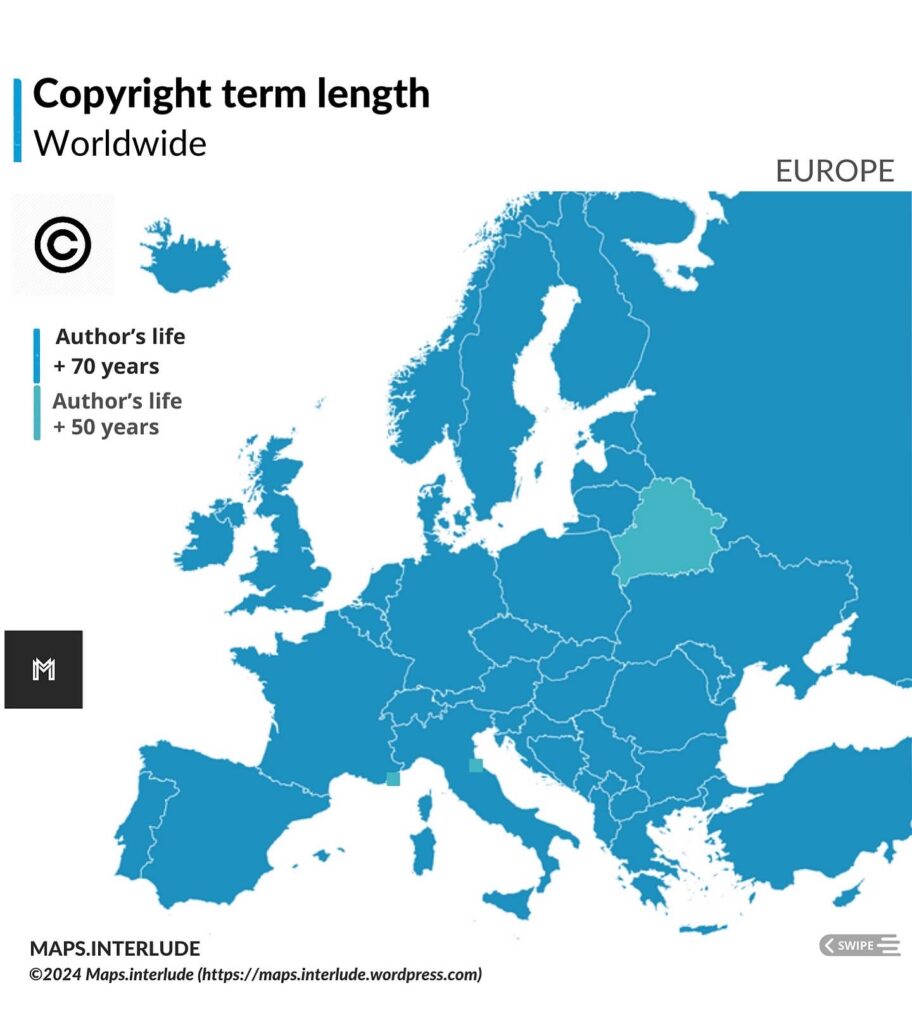
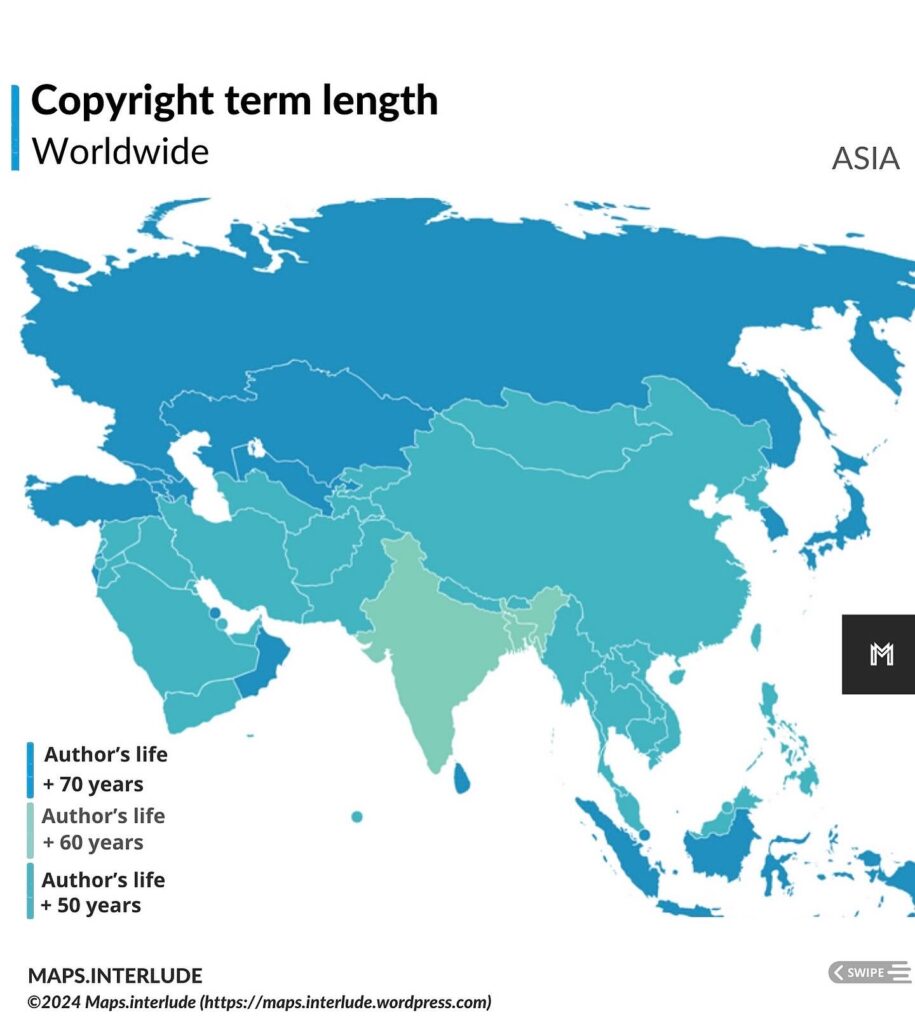
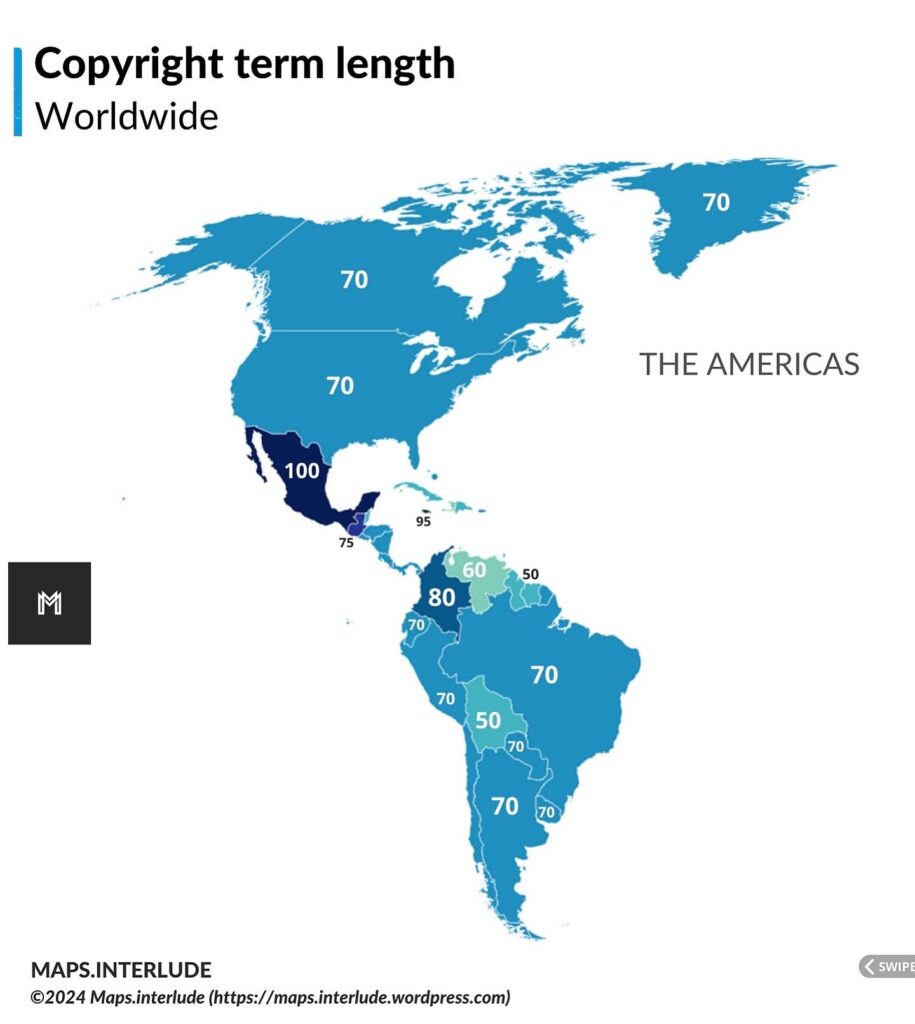
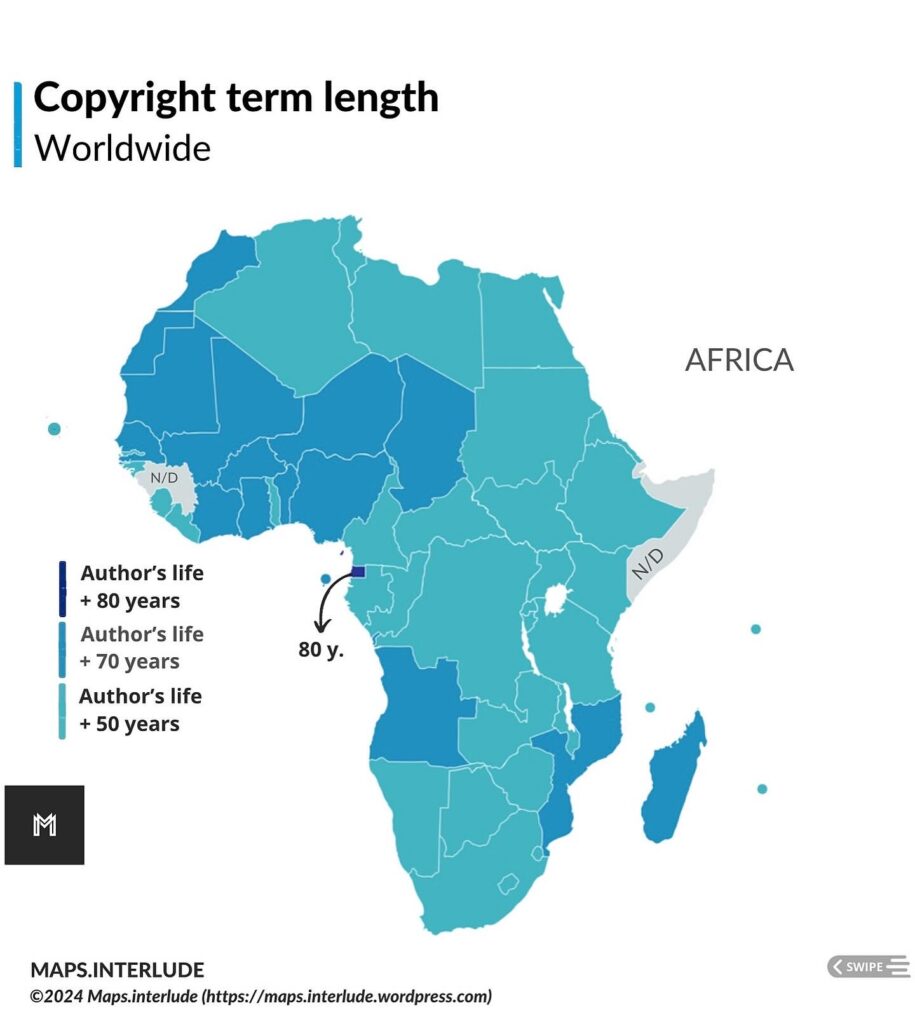
Under the Berne Convention, the duration of copyright depends on the length of the author’s life. Berne specifies that copyright exists a minimum of 50 years after the author’s death, while several countries, including the European Union and the United States, have extended that to 70 years after the author’s death. A few countries have extended copyright even further, with Mexico having the lengthiest term upto 100 years after the author’s death.

What is the violation of copyright?
The use or creation of content protected by a copyright without the owner’s consent is known as copyright infringement. A third party is violating the rights granted to the owner of the copyright, such as the right to the exclusive use of the work for a predetermined amount of time.
- Copyright infringement is the use or production of copyright-protected material without the permission of the copyright holder.
- Individuals and companies who develop new works register for copyright protection to ensure that they can profit from their efforts.
- Other parties may be granted permission to use those works through licensing arrangements.
- Other parties can also buy the works from the copyright holder.