I dedicate this page to my best friend Mercedes Aguiluz who wanted me to write about this topic
Fibromyalgia is a non-specific pain disorder whose current causes are unknown, although supplements are still being investigated for reducing this pain. Fibromyalgia (FM) is a syndrome that is mainly characterized by widespread chronic (>3 months) musculoskeletal pain. If severe enough, people with FM can have trouble performing activities of daily living, such as working or basic self-care tasks. Currently, there are no standard treatments
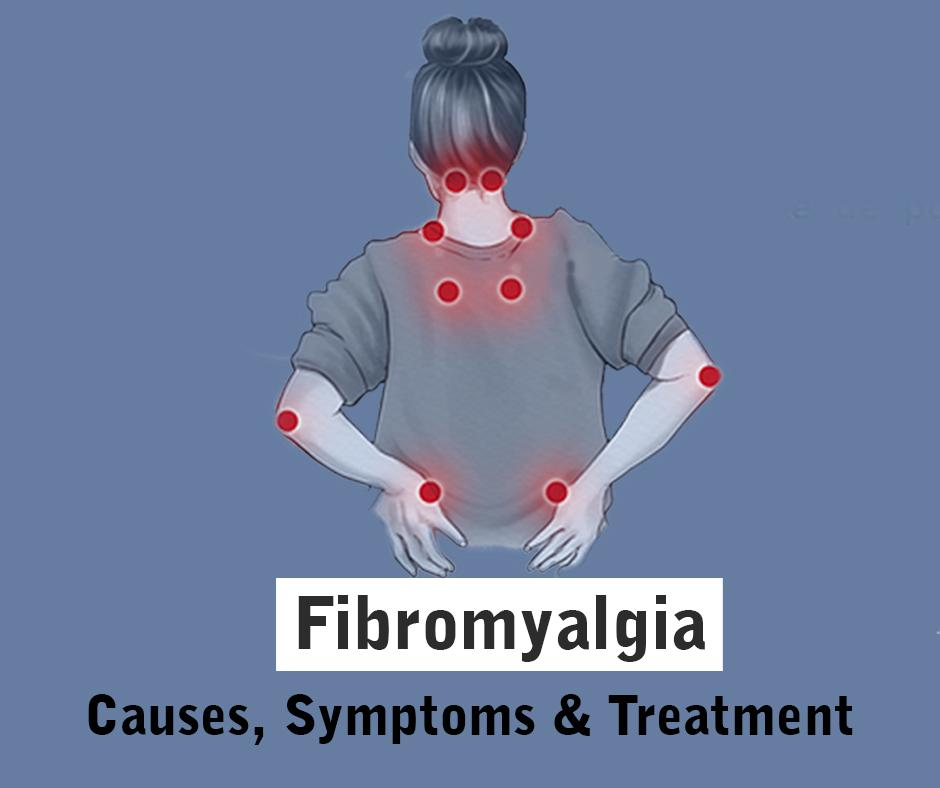
Signs and Symptoms of Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is known for causing widespread pain and tenderness throughout the body, as well as fatigue. It can also cause:
- Difficulty sleeping
- Problems with memory or concentration (“fibro fog”)
- Dizziness
- Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet
- Sensitivity to bright lights or loud noises
- Headaches
- Digestive issues
- Dry eyes or mouth
Because the symptoms of fibromyalgia overlap with those of many other conditions, diagnosing fibromyalgia can be difficult. In fact, it’s not uncommon to see several doctors and have many medical tests to rule out other conditions before getting a diagnosis of fibromyalgia.
Causes and Risk Factors of Fibromyalgia
- Researchers don’t know exactly what causes fibromyalgia, but it seems to occur when the body’s central and peripheral nervous systems don’t process pain properly. While pain in fibromyalgia may feel like it’s coming from a specific area of your body, it’s actually originating in your brain, specifically from the nervous system. Even though it’s often grouped with rheumatic diseases like arthritis and lupus, fibromyalgia isn’t considered to be a disease of inflammation or a joint or muscle disorder.
- It’s also not an autoimmune disorder — a condition in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues. Symptoms of fibromyalgia often begin after physical or emotional trauma, such as an illness, surgery, infection, stressful life event, or injury. Some experts believe these events may trigger the onset of the disorder, but it’s unclear exactly how this connection could be explained. Repeated stimulation may cause the brains of people with fibromyalgia to change — leading to an increase in chemicals known as neurotransmitters that signal pain.
- The actual pain receptors in the brain may also undergo changes, developing a kind of “memory” that leads them to overreact to pain signals.To complicate matters, fibromyalgia can also occur seemingly spontaneously, in the absence of trauma.Genetics may also play a role. Fibromyalgia is often seen in families, and having a relative with the disorder puts you at increased risk for it.
- But genes alone aren’t responsible for fibromyalgia.
How Is Fibromyalgia Diagnosed?
- Historically, fibromyalgia was diagnosed by having a doctor check 18 specific points on the body to see how many of them were painful when pressed firmly. This was called a “tender point” exam. However, doctors are moving away from the tender point exam in the diagnosis of fibromyalgia. Now, if you experience widespread pain — over a large area of your body — for more than three months, with no other possible cause, you’ll likely be diagnosed with the condition. At present, there are no tests that can be used to definitively diagnose fibromyalgia. However, your doctor may recommend a blood test to rule out other conditions. For example, a complete blood count (CBC) can rule out conditions such as anaemia, which can cause weakness and fatigue. This test and others like it will not confirm a fibromyalgia diagnosis, but they will effectively eliminate other possible causes for your symptoms.
- Diagnosis is based on a thorough clinical assessment by a healthcare provider. Currently, there are no tests to diagnose FM. Since FM symptoms can also be caused by many other health conditions, other causes must be ruled out. This is a diagnosis of exclusion.
Prognosis of Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia in and of itself doesn’t shorten life expectancy, according to a study published in 2018. Nor does it damage muscles or organs or directly cause death. However, risks for anxiety and depression are higher among people with fibromyalgia, which may also increase risk for suicide.In addition, people with the condition are also more likely to have diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure, among other health problems, which may lead to poorer overall health and quality of life.
Duration of Fibromyalgia
Although currently available treatments can help to manage the symptoms of fibromyalgia, there’s no cure for the condition. Many people with fibromyalgia live with widespread pain and debilitating fatigue for many years. As a result, the condition is a leading cause of disability and presents many challenges for people as they try to go about their day-to-day activities.Symptoms have also been known to worsen over time in some people with fibromyalgia, so taking steps to maintain overall health — including exercise, a healthy diet, and reducing stress — are particularly important for those with the condition.
A variety of types of medical specialists treat fibromyalgia. Some family practice doctors or internists (internal medicine specialists) can recognize and manage the condition. Other types of doctors who commonly treat fibromyalgia include:
- Pain management doctors, who treat all forms of pain, including that caused by fibromyalgia
- Rheumatologists, internists who specialize in treating arthritis and diseases of the joints, muscles, and soft tissues
- Neurologists, who treat diseases of the brain and nervous system
Before making an appointment with any of these specialists, ask whether they treat fibromyalgia. Not all pain management specialists, rheumatologists, or neurologists are knowledgeable about fibromyalgia. Fibromyalgia is often best treated with a combination of approaches.For some people, certain types of prescription medication can help reduce symptoms. For others, drugs have little effect, and for everyone, drugs have side effects that must be balanced with potential benefits.
Medication Options
No one medication works for all of the symptoms of fibromyalgia
LIFESTYLE CHANGE : What are some of the main medical treatments for fibromyalgia? FM is typically treated with a combination of lifestyle changes and pharmacological interventions.Lifestyle changes that may be implemented include:
Improving sleep
Gradually increasing physical activity
Stress management
Dietary changes
Cognitive behavioral therapy
DRUGS : However, some prescription drugs can help reduce the pain of the condition and improve sleep, which can help with fatigue. These are Antidepressants, Anticonvulsants, Muscle relaxants, Antipsychotics, and Medical Cannabis, But these medication options are for patients who do not see successful outcomes after stress reduction, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), exercise, and other nonmedication options.To date, three prescription medications have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) specifically to treat fibromyalgia:
- Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
- Pregabalin (Lyrica)
- Milnacipran (Savella)
Each of these drugs works differently, so talk to your doctor about which one may be right for your symptoms. Before starting you on a prescription medication, however, your doctor may recommend over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers, such as:
- acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- ibuprofen (Advil)
- naproxen (Aleve)
If these drugs don’t reduce your pain symptoms, your doctor may recommend a prescription pain reliever. However, opioid-based pain relievers aren’t recommended for people with fibromyalgia, as they can lead to dependence and may even worsen your pain over time.In addition, certain types of antidepressants have been found to work on fibromyalgia pain and reduce fatigue. Other antidepressants can help you sleep better.
Your doctor may also suggest muscle relaxants or even anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) to relieve pain.
The treatment must be tailored to the individual’s responses to any of the previously mentioned interventions
…….YET WRITING
Very soon I will complete this topic
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Question: Have any supplements been studied for fibromyalgia?
Since there are no standard treatments for FM, dietary supplements are often used to ameliorate symptoms. The supplements with the greatest amount of research are vitamin-d and coenzyme-q10. With that being said, the findings are inconsistent and more evidence is needed before recommendations can be made.
Question: Are there any other treatments for fibromyalgia?
If initial therapies are not effective, people with FM may pursue alternative treatments to reduce symptoms. These treatments include:
- Massage
- Chiropractic
- Acupuncture
The evidence surrounding these interventions is scarce. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional before implementing any alternative treatments.
Question: How could diet affect fibromyalgia?
Some studies found that dietary changes can improve symptoms of FM. However, the quality of these studies was poor and varied in their dietary interventions. More randomized controlled trials are needed to understand the relationship between diet and FM
References
^Rosalba Siracusa, Rosanna Di Paola, Salvatore Cuzzocrea, Daniela ImpellizzeriFibromyalgia: Pathogenesis, Mechanisms, Diagnosis and Treatment Options UpdateInt J Mol Sci.(2021 Apr 9)
^Daniel J ClauwFibromyalgia: a clinical reviewJAMA.(2014 Apr 16)
^The content of this page was partially adapted from MedlinePlus of the National Library of Medicine
^Laura Tomaino, Lluís Serra-Majem, Stefania Martini, Maria Rosaria Ingenito, Paola Rossi, Carlo La Vecchia, Fabrizia Bamonti, Luisella VignaFibromyalgia and Nutrition: An Updated ReviewJ Am Coll Nutr.(Sep-Oct 2021)
^Giuditta Pagliai, Ilaria Giangrandi, Monica Dinu, Francesco Sofi, Barbara ColombiniNutritional Interventions in the Management of Fibromyalgia SyndromeNutrients.(2020 Aug 20)