What Exactly Is Modulation?
- Author: GREAT MASTER VIKRANT ROHIN
- Date: MAY 3, 2023
The ability of human genius is the transmission of information over long distances via communication systems. We can communicate with, video chat with, and text with anyone on the planet. To increase the reach of the signals, the communication system employs a very clever technique known as modulation.
This article will explain what modulation is and why it is necessary.
Section I: Table of Contents
- Modulation
- What is the purpose of modulation?
- Wireless Communication Interference from Other Signals Antenna Size
- FAQS
Modulation
Modulation is the process of converting data into electrical signals optimized for transmission.
The modulation process involves two signals. The message signal, also known as the baseband signal, is the frequency band that represents the original signal. This is the signal that will be sent to the receiver. Typically, the frequency of such a signal is low. A high-frequency sinusoidal wave is also involved in this. This signal is referred to as the carrier signal. Carrier signals almost always have a higher frequency than baseband signals. The baseband signal’s amplitude is transferred to the high-frequency carrier. A high-frequency carrier can travel much further than a baseband signal. Thus, modulation is the process of superimposing a low-frequency signal on a high-frequency carrier signal.
Modulation types?
- Modulation techniques are roughly divided into four types: Analog modulation, Digital modulation, Pulse modulation, and Spread spectrum method.
One more way of division of Modulation:
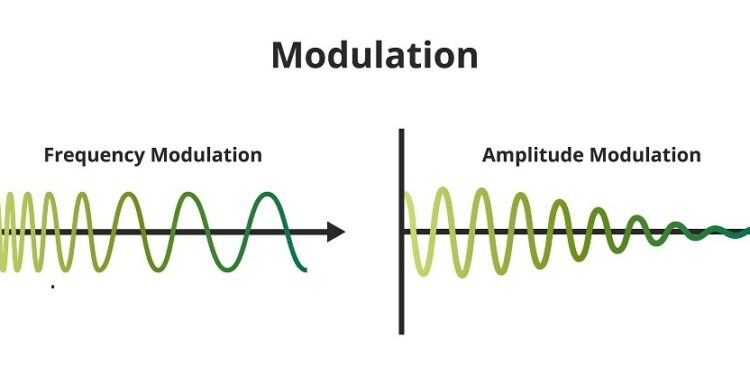
- Amplitude Modulation
- Frequency Modulation
- Phase Modulation
What is the Importance of Modulation?
We live in a digitally advanced era where the need for wires is no longer a necessity to be connected to everyone. Messages, information, and signals are sent from one part of the world to another within minutes. The modulation process plays a major role in the fast transmission of signals. Below, we have mentioned a few of their importance in the communication system:
Size of the Antennae
When a signal is transmitted over free space, the antennae radiate it, and the receiver receives it. To operate efficiently, antennae must be of the order of the wavelength of the transmitted signal.
Wireless Communication
We have eliminated the need for wires in communication systems by using modulation to transmit signals over long distances through space. Modulation enabled humans to become wireless. Telephones were no longer required to be plugged into a wall. Using a mobile phone went from a pipe dream to the next big thing.
Interference from Other Signals
This is a practical point. Assume you send the baseband signal to a receiver, say your friend’s phone. Thousands of people will be using their mobile phones in the city, just like you. There is no way to distinguish such signals, and they will interfere with each other, resulting in a lot of noise in the system and a very poor output. There is no signal mixing because a carrier wave of high frequencies is used and a band of frequencies is assigned to each message, and the received signals are absolutely perfect.

Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is amplitude modulation?
It is a type of modulation in which the carrier signal’s amplitude varies in proportion to the message signal while the phase and frequency remain constant.
Define frequency modulation.
The carrier signal frequency is changed in proportion to the message signal in this modulation. The constant phase and amplitude are referred to as frequency modulation.
Define demodulation.
The process of extracting the original information-carrying signal from a modulated carrier wave is known as demodulation. A demodulator is an electronic circuit that recovers information from a modulated carrier wave.